Why access to finance key to Nigeria’s socio-economic- Analysts

Again, finance analysts have reiterated that access to finance is key to the socio-economic growth of the country, however, identified that increase loans to individuals and SMEs without suffering the fall-out of bad debt is a challenge.
The Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) increased the minimum loan-to-deposit ratio (LDR) of commercial banks from 60 per cent to 65 per cent in the latter part of 2019.
According to a Bloomberg report, the measure was among a raft of regulations aimed at forcing banks to boost credit, mainly to farmers, small-and-medium-size businesses and consumers.
Analysts at CredoLab said that the LDR is used to assess a bank’s liquidity by comparing a bank’s total loans to its total deposits for the same period.
The LDR is expressed as a percentage. If the ratio is too high, it means that the bank may not have enough liquidity to cover any unforeseen fund requirements. Conversely, if the ratio is too low, the bank may not be earning as much as it could be earning.
According to the report, Nigeria’s banks are some of the most reluctant lenders in major emerging markets, with an average Loan-to-Deposit Ratio (LDR) (below 60 per cent. That compares with 78per cent across Africa, according to data compiled by Bloomberg, with 90 per cent in South Africa and about 76 per cent in Kenya.
Compare this with developed markets such as the UK, which according to Statista.com, states that Shawbrook Bank’s loan to deposits ratio on the British market between 2012 and 2016 increased from 74 per cent in 2012 to 102.7 per cent as of 2016.
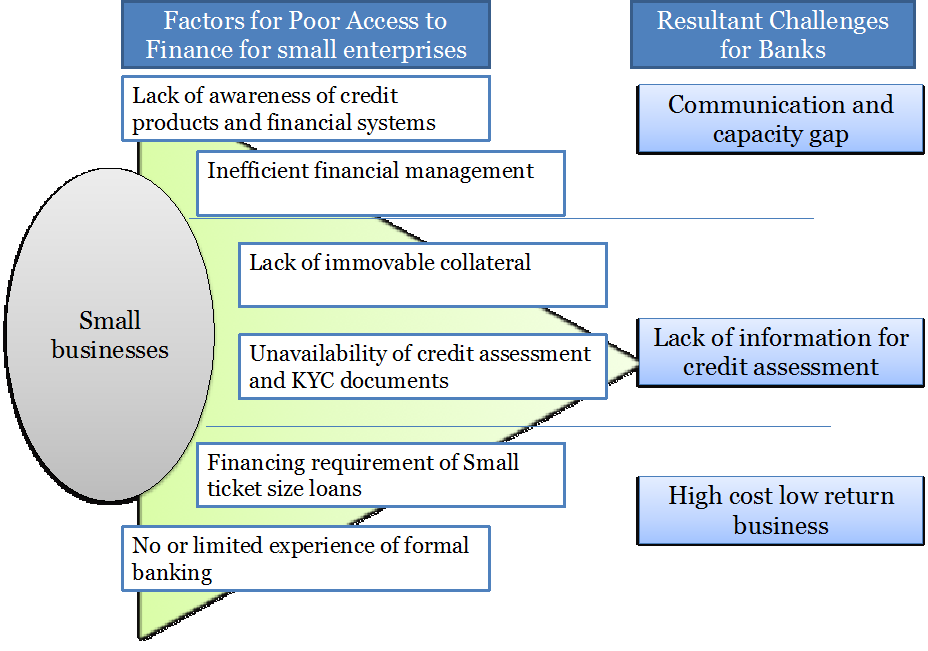
The Director-General, Lagos Chamber of Commerce and Industry (LCCI), Mr Muda Yusuf, had stated that the greatest challenge business operators in the country have been facing over the years was access to credit, which he said had resulted to huge financing gaps.
In order to expedite this LDR, new digital banks and progressive lending institutions in emerging economies are looking at using technology to expedite the process, such as digital scoring methods based on Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, where smartphone device metadata solutions, such as offered by CredoLab and other providers, is used to assessing credit-worthiness instead of traditional methods.
Tarun Kumar Kalra, Global Head of Sales at CredoLab cited a successful example in Indonesia, which has one of the largest pool of unbanked customers in the world.
One of the top 10 Indonesian banks serving over two million customers wanted to leverage the opportunities in this pool of unbanked customers. The bank had a comprehensive array of products and services being delivered through physical branches, mobile and web banking.
The bank’s mandate was to increase the number of loans it disbursed to the new-to-bank (NTB) customers by using an underwriting process that was fair to the applicants and yet highly predictable of their behaviour,” he said.
There were several challenges, such as increasing approval rates, 85per cent of the applicants being rejected and the low predictability of the existing underwriting process,” he added. “The bank solved this problem by introducing digital scorecards based on smartphone device data, which led to a +107 per cent approval rate, user adoption of 61per cent and an average of five seconds to approve the application.”
Kalra said that what’s noteworthy in the deployment of this solution was the short period of 2 weeks that it took for the bank to implement the new credit scoring system, as there were no development time or costs, while at the same time meeting local data security and privacy laws and regulations.
Asked about the uptake of digital smartphone metadata credit scoring methodology, Kalra responded that over 61 lending institutions have adopted CredoLab’s technology across emerging economies in the Asia Pacific region.
“With our launch into Africa, specifically in South Africa, Nigeria and Kenya last year, we already have three major traditional and digital banks leveraging the technology in South Africa. Financial institutions in Nigeria and Kenya are investigating this technology as a secure and sustainable way of expanding credit into the unbanked markets, and raising banks’ Loan to Deposit Ratio while minimising risk,” he concluded.







